Adhering To The Enterprise Spirit Of "Integrity, Harmony, Pragmatism And Innovation"
1. Defect name: stomata

|
Welding mode |
Cause of occurrence |
Preventive measure |
|
Manual arc welding |
(1) Bad or wet electrode. (2) The weldment has moisture, oil or rust. (3) The welding speed is too fast. (4) Current is too strong. (5) Arc length is not suitable. (6) The thickness of the weldment is large, and the metal is cooled too fast. |
(1) Select the appropriate electrode and pay attention to drying. (2) Clean the welded part before welding. (3) Reduce the welding speed so that the internal gas is easy to escape. (4) The manufacturer recommends appropriate current. (5) Adjust the appropriate arc length. (6) Implement appropriate preheating work. |
|
CO2 gas shielded welding |
(1) The base material is unclean. (2) The welding wire is rusty or the welding flux is wet. (3) Poor spot welding, improper selection of welding wire. (4) The dry extension length is too long, and the CO2 gas protection is not thorough. (5) Large wind speed, no windscreen. (6) The welding speed is too fast and the cooling is fast. (7) The spark splash sticks to the nozzle, causing gas turbulence. (8) Poor gas purity, containing more debris (especially containing water). |
(1) Pay attention to clean the welded part before welding. (2) Choose the appropriate welding wire and pay attention to keep dry. (3) Spot welding bead should not be defective, and it should be clean, and the size of the welding wire should be appropriate. (4) Reduce the dry stretch length and adjust the appropriate gas flow. (5) Install windscreen equipment. (6) Reduce the speed so that the internal gas escapes. (7) Pay attention to remove the welding slag at the nozzle, and apply the splash adhesion prevention agent to extend the life of the nozzle. (8) The purity of CO2 is more than 99.98%, and the moisture is less than 0.005%. |
|
Submerged arc welding |
(1) The weld has rust, oxide film, grease and other organic impurities. (2) The flux is wet. (3) The flux is contaminated. (4) Welding speed is too fast. (5) Insufficient flux height. (6) The height of the flux is too large, so that the gas is not easy to escape (especially in the case of fine flux particle size). (7) The welding wire is rusty or stained with oil. (8) The polarity is not appropriate (especially in the butt will be polluted will produce pores). |
(1) The weld should be ground or burned with flame, and then removed with a wire brush. (2) Drying at about 300℃ (3) Pay attention to the storage of flux and the cleaning of the area near the welding site, so as not to mix with debris. (4) Reduce the welding speed. (5) The flux outlet rubber pipe mouth should be adjusted higher. (6) The flux outlet rubber pipe should be adjusted lower, and the appropriate height should be 30-40mm in the automatic welding situation. (7) Change to clean welding wire. (8) Change the direct current connection (DC-) to the direct current reverse connection (DC+). |
|
Poor equipment |
(1) Pressure table cooling, gas can not flow out. (2) The nozzle is blocked by the spark splash. (3) The welding wire has oil and rust. |
(1) When the gas regulator is not attached to an electric heater, it is necessary to install an electric heater and check the flow rate of the table. (2) Often remove nozzle spatter. And coated with splash attachment prevention agent. (3) Do not touch oil when storing or installing welding wire. |
|
Self-protecting flux-cored wire |
(1) The voltage is too high. (2) The protruding length of the welding wire is too short. (3) Corrosion, paint and moisture on the surface of the steel plate. (4) The torch drag Angle is tilted too much. (5) The moving speed is too fast, especially transverse welding. |
(1) Reduce the voltage. (2) Use according to various welding wire instructions. (3) Clean before welding. (4) Reduce the drag Angle to about 0-20°. (5) Appropriate adjustment. |
2. Defect name: bite edge

3.Defect name: slag inclusion
Welding mode
Cause of occurrence
Preventive measure
Manual arc welding
(1) The current is too strong.
(2) The welding rod is not suitable.
(3) The arc is too long.
(4) Improper operation method.
(5) The base material is unclean.
(6) overheating of the base material.
(1) Use a lower current.
(2) Select the appropriate type and size of electrode.
(3) Maintain appropriate arc length.
(4) Use the correct Angle, slower speed, shorter arc and narrower operation method.
(5) Remove oil stains or rust from the base material.
(6) Use a small diameter electrode.
CO2 gas shielded welding
(1) The arc is too long and the welding speed is too fast.
(2) When fillet welding, the welding rod alignment position is not correct.
(3) The vertical welding swing or poor operation, so that the two sides of the weld pass fill insufficient edge.
(1) Reduce arc length and speed.
(2) In horizontal fillet welding, the position of the welding wire should be 1-2mm away from the intersection point.
(3) Correct the operation method.
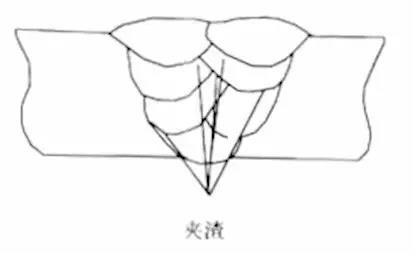
4.Defect name: not welded through
Welding mode
Cause of occurrence
Preventive measure
Manual arc welding
(1) The welding slag of the front layer is not completely removed.
(2) Welding current is too low.
(3) The welding speed is too slow.
(4) The electrode swing is too wide.
(5) Poor weld combination and design.
(1) Thoroughly remove the welding slag of the front layer.
(2) Adopt higher current.
(3) Improve the welding speed.
(4) Reduce the swing width of the electrode.
(5) Correct the appropriate groove Angle and clearance.
CO2 gas arc welding
(1) The base metal is inclined (downhill) so that the welding slag is advanced.
(2) After the previous welding, the welding slag is not clean.
(3) The current is too small, the speed is slow, and the welding amount is much.
(4) The forward welding method is used, and the welding slag in the slot is very advanced.
(1) Place the weldment in a horizontal position as far as possible.
(2) Pay attention to the cleanliness of each pass.
(3) Increase the current and welding speed, so that the welding slag is easy to float.
(4) Improve the welding speed.
Submerged arc welding
(1) The welding direction is inclined toward the base material, so the welding slag flow is advanced.
(2) When multi-layer welding, the slotted surface is dissolved into the welding wire, and the welding wire is too close to the slotted side.
(3) Slag inclusion is easy to occur at the starting point of welding with a guide plate.
(4) The current is too small, and welding slag remains between the second layer, which is easy to crack when welding the sheet.
(5) The welding speed is too low, so that the welding slag is advanced.
(6) The arc voltage of the final finishing layer is too high, causing the free welding slag to churn at the end of the weld.
(1) The welding is changed to the opposite direction, or the base material is changed to the horizontal direction as far as possible.
(2) The distance between the slotted side and the welding wire should be at least greater than the diameter of the welding wire.
(3) The thickness and groove shape of the guide plate should be the same as that of the base material.
(4) Improve the welding current, so that the residual welding slag is easy to melt.
(5) Increase welding current and welding speed.
(6) Reduce the voltage or increase the welding speed, and change the cover layer from single pass welding to multi-pass welding if necessary.
Self-protecting flux-cored wire
(1) Arc voltage is too low.
(2) Improper swing of the welding wire.
(3) The welding wire is extended too long.
(4) The current is too low and the welding speed is too slow.
(5) The first welding slag is not fully removed.
(6) The first combination is poor.
(7) The groove is too narrow.
(8) The weld is tilted downward.
(1) Appropriate adjustment.
(2) Practice more.
(3) According to various welding wire instructions.
(4) Adjust welding parameters.
(5) Completely clear
(6) Use the appropriate voltage and pay attention to the swing arc.
(7) Correct the appropriate groove Angle and clearance.
(8) Put flat, or move faster.
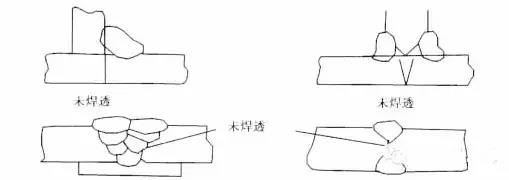
5.Defect name: Crack
Welding mode
Cause of occurrence
Preventive measure
Manual arc welding
(1) Improper selection of welding rods.
(2) Current is too low.
(3) The welding speed is too fast and the temperature rise is not enough, and the arc impulse is blocked by the welding slag and cannot be given to the base material.
(4) Incorrect weld design and combination.
(1) Choose a more permeable electrode.
(2) Use appropriate current.
(3) Use the appropriate welding speed.
(4) Increase the number of slots, increase the gap, and reduce the root depth.
CO2 gas shielded welding
(1) The arc is too small and the welding speed is too low.
(2) The arc is too long.
(3) Poor slotting design.
(1) Increase welding current and speed.
(2) Reduce arc length.
(3) Increase the number of slots. Increased clearance reduces root depth.
Self-protecting flux-cored wire
(1) Current is too low.
(2) The welding speed is too slow.
(3) Voltage is too high.
(4) Improper pendulum arc.
(5) Improper Angle of groove.
(1) Increase the current.
(2) Improve the welding speed.
(3) Reduce the voltage.
(4) Practice more.
(5) The grooving Angle is larger.

6.Defect name: deformation
Welding mode
Cause of occurrence
Preventive measure
Manual arc welding
(1) Welded parts contain too high carbon, manganese and other alloying elements.
(2) The quality of the electrode is poor or wet.
(3) weld restraint stress is too large.
(4) The material of the mother strip contains too much sulfur and is not suitable for welding.
(5) Insufficient preparation for construction.
(6) The base material thickness is large, and the cooling speed is too fast.
(7) Current is too strong.
(8) The first pass is insufficient to resist shrinkage stress.
(1) Use low hydrogen electrode.
(2) Use appropriate welding rods and pay attention to drying.
(3) Improve the structural design, pay attention to the welding sequence, and heat treatment after welding.
(4) Avoid using bad steel.
(5) Preheating or post-heating should be considered when welding.
(6) Preheat the base metal, slow cooling after welding.
(7) Use appropriate current.
(8) The welded metal of the first weld shall fully resist the shrinkage stress.
CO2 gas shielded welding
(1) The slot Angle is too small, and pear-shaped and bead cracks are generated during high current welding.
(2) The carbon content of the base material and other alloys are too high (welding pass and thermal shadow zone).
(3) When multi-layer welding, the first layer weld pass is too small.
(4) Improper welding sequence, resulting in too strong binding force.
(5) The welding wire is wet, and hydrogen is invading the weld bead.
(6) The sleeve plate is poorly connected, resulting in uneven and stress concentration.
(7) Due to excessive welding of the first layer, the cooling is slow (stainless steel, aluminum alloy, etc.).
(1) Pay attention to the appropriate slotting Angle and current coordination, if necessary to increase the slotting Angle.
(2) The use of low carbon electrode.
(3) The first welded metal must be sufficiently resistant to shrinkage stress.
(4) Improve the structural design, pay attention to the welding sequence, and heat treatment after welding.
(5) Pay attention to the preservation of welding wire.
(6) Pay attention to the precision of the weldment combination.
(7) Pay attention to the correct current and welding speed.
Submerged arc welding
(1) The combination of the welding wire and flux used in the weld base material is inappropriate (the carbon content of the base material is too large, and the manganese content of the welding wire metal is too small).
(2) Rapid cooling of the weld bead causes hardening of the heat-affected zone.
(3) The welding wire contains too much carbon and sulfur.
(4) The bead force generated in the first layer of multi-layer welding is insufficient to resist the shrinkage stress.
(5) Too deep penetration or segregation in fillet welding.
(6) The welding construction sequence is not correct, and the binding force of the base metal is large.
(7) The shape of the pass is inappropriate, and the ratio of the width of the pass to the depth of the pass is too large or too small.
(1) The use of welding wire with higher manganese content, in the base material with a lot of carbon, there should be preheating measures.
(2) The welding current and voltage should be increased, the welding speed should be reduced, and the base material should be heated.
(3) Replace the welding wire.
(4) The welding metal of the first layer of weld must fully resist shrinkage stress.
(5) Reduce the welding current and welding speed and change the polarity.
(6) Pay attention to the specified construction method, and give the welding operation construction guidance.
(7) The ratio of weld width to depth is about 1:1:25, the current is reduced, and the voltage is increased.

Welding mode
Cause of occurrence
Preventive measure
Manual welding
CO2 gas shielded welding
Self-protecting flux-cored wire welding
Automatic submerged arc welding
(1) Too many welding layers.
(2) Improper welding sequence.
(3) Insufficient preparation for construction.
(4) Base metal cooling speed.
(5) overheating of the base material. (sheet)
(6) Improper weld design.
(7) Welding too much metal.
(8) The mode of restraint is not true.
(1) Use large diameter electrode and high current.
(2) Correct the welding sequence
(3) Before welding, use a fixture to fix the weldment to avoid warping.
(4) Avoid cooling too fast or preheating the base metal.
(5) Select welding materials with low penetration.
(6) Reduce the weld gap and reduce the number of slots.
(7) Pay attention to the welding size, do not make the welding pass too large.
(8) Pay attention to the fixed measures to prevent deformation.
TEL:+86-317-6165555 6689999
E-mail:sales@longshengpiping.com
ADD:YANGLONGTAN VILLAGE BIANWU TOWN YANSHAN COUNTY, HEBEI PROVINCE CHINA